
Many parents wonder whether teething can cause ear infections, as the symptoms can look almost identical at times.
The ear infection vs. teething question becomes even trickier when drooling, irritability, and constant ear touching all appear together.
Once you understand how these two issues overlap and differ, it becomes much easier to tell what your child needs.
This clarity helps caregivers feel more confident and less worried when trying to figure out the cause of their little one’s discomfort.
Common Teething Symptoms Parents Need to Know
Teething can cause a wide range of symptoms that leave babies uncomfortable and parents unsure of what’s really going on.
Recognizing these patterns makes it easier to tell typical teething behavior from signs of something more serious.
- Excessive Drooling: Many babies drool nonstop during teething, often soaking through bibs and clothing
- Chewing on Objects: Babies instinctively bite toys, hands, or anything they can reach to ease gum pressure
- Swollen, Tender Gums: Gums may appear puffy or red and feel sensitive when touched
- Irritability and Fussiness: Discomfort in the gums often makes babies more cranky than usual
- Mild Fever Below 101°f: A slight rise in temperature is common, but anything above 101°F may indicate illness
- Ear Pulling or Rubbing: This is referred to as pain from the gums, leading many parents to wonder about ear infections
- Sleep Disruptions: Babies may wake more often or struggle to settle due to gum discomfort
- Decreased Appetite: Sore gums can make feeding uncomfortable, causing temporary dips in appetite
Understanding Ear Infections in Children
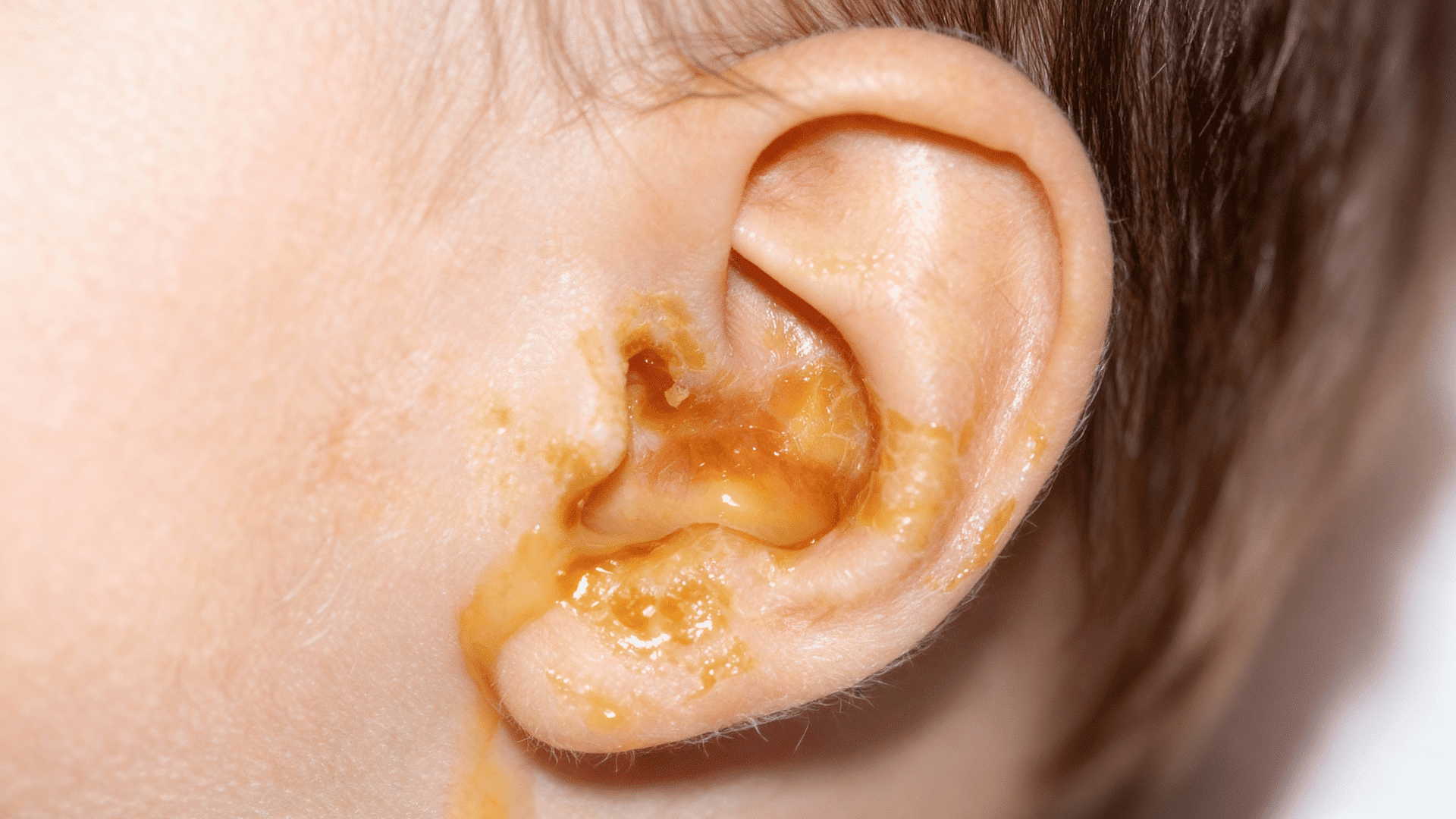
An ear infection, or acute otitis media, occurs when bacteria or viruses enter the middle ear, leading to fluid buildup behind the eardrum.
When the Eustachian tubes become blocked or fail to drain properly, fluid builds up behind the eardrum and creates the perfect environment for bacteria or viruses to grow.
Babies and toddlers experience this more often because their Eustachian tubes are shorter, narrower, and more horizontally oriented, making drainage much harder.
Their immune systems are also still developing, so they are less equipped to fight off infections.
While parents often ask, can teething cause ear infections, ear infections are mainly linked to these structural and immune-related factors, not teething itself.
Common Ear Infection Symptoms
Recognizing ear infection symptoms helps parents distinguish between teething discomfort and a condition requiring medical treatment. Here’s what to watch for:
- High Fever (over 101°f-102°f): Ear infections often spike fevers that need monitoring
- Persistent Ear Pulling/tugging: This goes beyond occasional rubbing and becomes constant, distressed behavior
- Crying/inconsolable Behavior: The pain from pressure buildup makes babies difficult to be comforted
- Fluid Drainage from The Ear: Yellow, white, or bloody discharge signals that the eardrum may have ruptured from pressure
- Trouble Sleeping (worse when Lying Down): Horizontal positions increase ear pressure, intensifying pain significantly
- Loss of Balance: Fluid in the middle ear affects equilibrium, causing wobbliness or clumsiness
- Hearing Difficulties: Fluid blocks sound waves, making babies seem unresponsive or turning up the volume on toys
- Cold Symptoms Before/during Infection: Congestion often precedes ear infections as viruses spread through connected passages
How to Treat Ear Infections in Children at Home
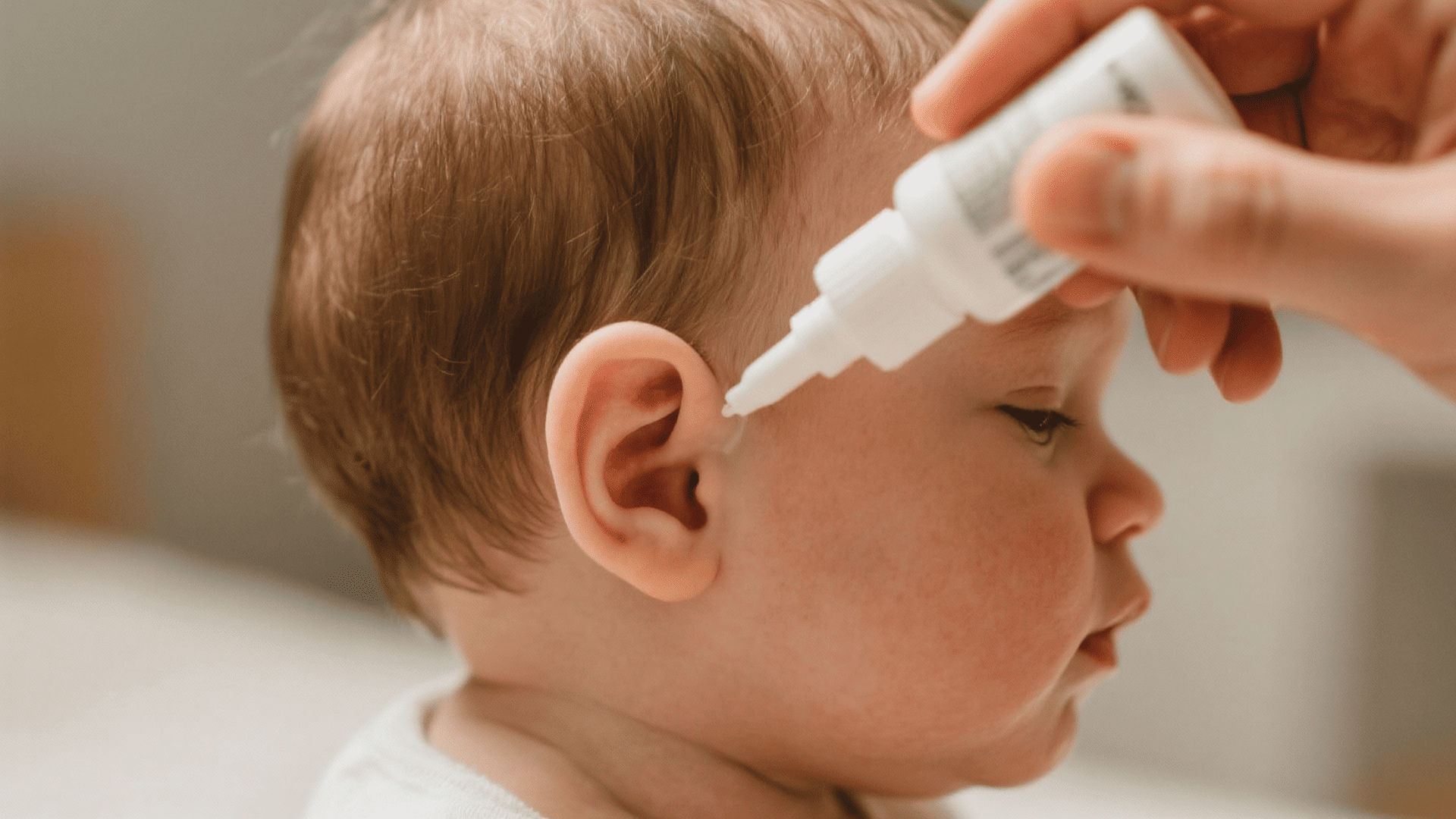
While parents often wonder if teething can cause ear infections, these remedies work regardless of the underlying trigger. Always consult your pediatrician before trying new treatments.
1. Warm Compress
Holding a warm, damp cloth against the affected ear for 10 to 15 minutes can provide quick, gentle relief. The warmth helps improve circulation around the ear, which may reduce pressure and soothe pain.
Many parents find this especially helpful before naps or bedtime, when ear discomfort tends to worsen. Always ensure the compress is warm, not hot, to avoid irritation.
2. Age-Appropriate Pain Relief
Medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help ease both pain and fever associated with an ear infection. These are commonly recommended by pediatricians and often bring noticeable comfort.
Always follow proper dosing guidelines based on your child’s age and weight. If you are unsure, double-check with your healthcare provider before giving any medication.
3. Upright Resting Position
Keeping your child propped up with pillows during rest can make a big difference in how they feel. Lying flat increases pressure in the middle ear, which can worsen pain.
An upright position helps fluid drain more effectively and reduces discomfort. This technique is often recommended during both naps and quiet time.
4. Extra Fluids
Encouraging your child to drink water, breast milk, or formula helps thin mucus and supports better Eustachian tube function.
When fluids are thinner, they can drain more easily from the middle ear, which reduces pressure and pain. Frequent small sips can be easier for little ones. Hydration also supports overall recovery.
5. Raised Sleep Position
Keeping your child’s head slightly elevated during sleep can help minimize pressure buildup in the ears. This is especially helpful at night when symptoms tend to intensify.
Use a safe, gradual incline, such as raising the head of the crib mattress slightly, not by adding loose pillows. Proper elevation can help your child sleep more comfortably and reduce nighttime awakenings.
Teething Vs Ear Infection
Telling the difference between teething and an ear infection can be challenging because many symptoms overlap. A clear comparison can help parents understand what is normal discomfort and what may require medical attention.
| Sign | Teething | Ear Infection |
|---|---|---|
| Fever | Mild or none | Often higher than 100.4°F |
| Pain source | Gums and jaw | Middle ear pressure |
| Ear pulling | Common | More intense and persistent |
| Sleep | Light disruption | Worsens when lying down |
| Relief | Improves with chewing or cold toys | Little relief from teething remedies |
Community Discussions on Teething Causing Ear Infections
Below are some of the most frequently asked questions found across communitythreads like Reddit and Quora, along with simple one-line answers drawn from those discussions.
Many discussions revolve around common questions, such as whether teething can cause ear infections, and the shared insights help parents understand what is normal and what needs medical attention.
1. What are the signs of teething in babies?
Teething usually brings drooling, swollen gums, chewing on objects, fussiness, and mild temperature changes.
2. How can you tell the difference between teething and an earache?
Teething pain is gum-centered and eases with chewing, while earache pain worsens when lying down and may be accompanied by fever.
3. What should parents do if they suspect teething discomfort?
Offer chilled teethers, gentle gum massage, and pediatrician-approved pain relief if needed.
4. What should parents do if they suspect an ear infection?
Have the child evaluated by a pediatrician, as only an otoscopic exam can confirm an infection.
5. Can ear pulling alone tell you what the problem is?
No, because babies pull their ears during both teething and infections, so other symptoms need to be considered.
Can Teething Make an Existing Ear Infection Feel Worse?
Yes, teething can heighten sensitivity throughout the jaw and ear area, making an existing ear infection feel more intense.
When gum pain and ear pressure happen simultaneously, they create a compounding effect that amplifies the child’s overall discomfort.
The nerves in the jaw, gums, and ears are interconnected, so inflammation in one area can worsen the others. Teething doesn’t directly trigger infections; it can make existing symptoms appear more severe.
Children might cry harder, pull their ears more frequently, and seem inconsolable. Once these conditions naturally overlap, distinguishing between them becomes challenging, which is why medical evaluation is important.
Preventive Tips for Ear Infections
Ear infections are common in young children, but many can be reduced or avoided with simple daily habits. Here are the most widely recommended tips:
- Stay up To Date on Vaccinations: Helps prevent illnesses that commonly lead to ear infections
- Avoid Secondhand Smoke: Reduces irritation in the Eustachian tubes
- Practice Good Hand Hygiene: Limits the spread of cold and flu viruses
- Breastfeeding when Possible: Supports a stronger immune system
- Keep Your Child Upright During Feedings: Prevents milk from entering the middle ear
- Limit Pacifier Use After 6 Months: Overuse can increase the risk of middle ear infections
- Manage Allergies Promptly: Reduces inflammation and mucus buildup that can trigger ear problems
- Keep Sick Contacts Minimized: Reduces exposure to respiratory infections that often lead to ear infections
The Key Takeaway
While teething and ear infections share overlapping symptoms, they’re distinct conditions requiring different approaches.
Can teething cause ear infections? Not directly, but teething can worsen existing ear discomfort and make symptoms appear more severe.
Parents should monitor fever levels, sleep patterns, and persistent pain to determine what’s really happening.
Once natural symptoms escalate, especially high fevers, fluid drainage, or inconsolable crying, it’s time to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
